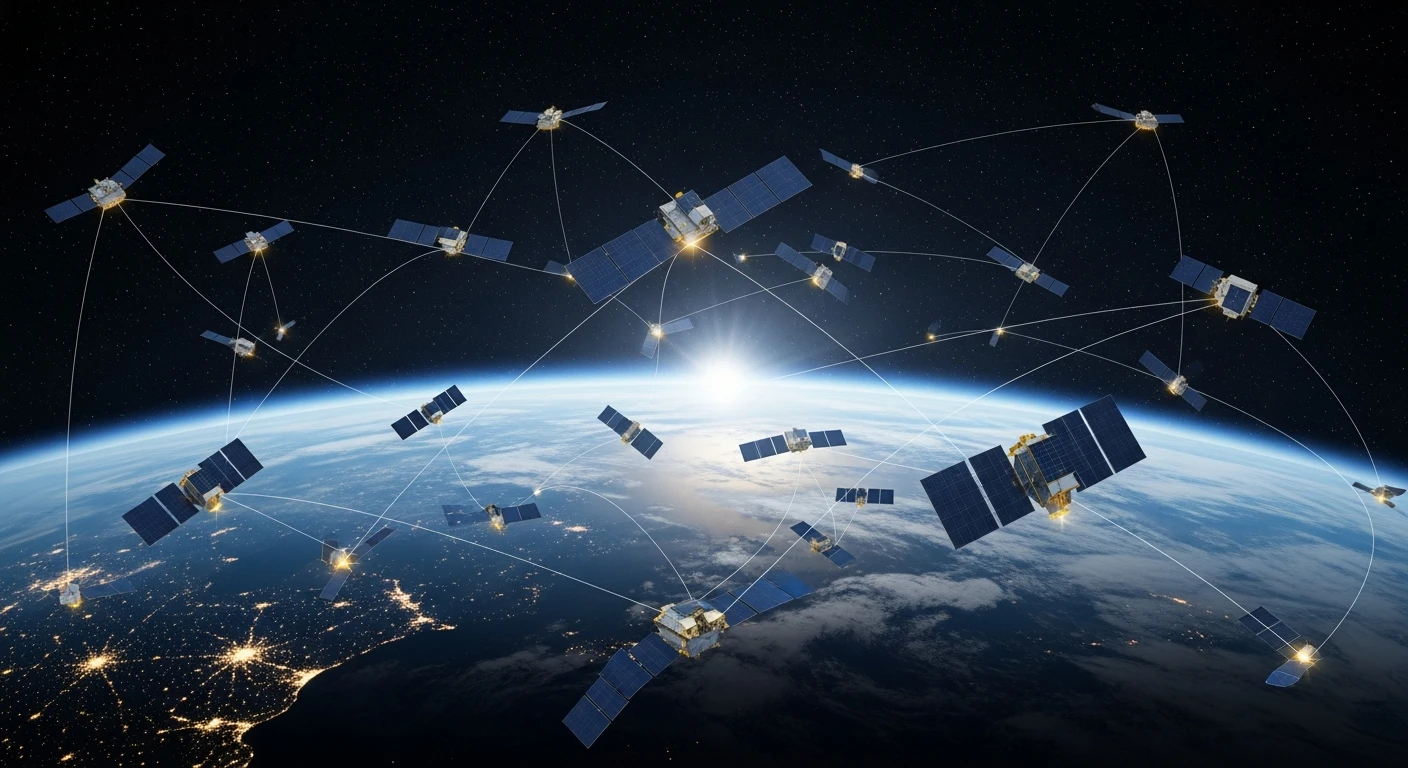
While the global telecommunications industry is still heavily invested in maximizing the deployment and return on 5G networks, a more strategic and far-reaching competition is rapidly accelerating behind the scenes to define its successor. The development of sixth-generation wireless technology, or 6G, represents a paradigm shift that extends far beyond incremental increases in speed and bandwidth. It is envisioned as the foundational infrastructure for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, promising to create an intelligent, seamlessly integrated digital ecosystem connecting humans, machines, and the physical environment in ways previously confined to science fiction. This global race is not merely about technological supremacy; it is a geopolitical and economic imperative, with nations and corporations vying to set the standards that will govern the next era of digital interaction and innovation. The stakes are incredibly high, as the architecture of 6G will dictate the future of autonomous systems, smart cities, and a globally interconnected society.
1. Charting the Course for a New Communications Paradigm
The overarching vision for 6G is transformative, aiming to build upon the advancements of its predecessor to unlock a future of ubiquitous, intelligent connectivity. This next generation is set to deliver unprecedented performance, with projections including data speeds exceeding 100 Gbps and ultra-low latency that approaches the instantaneous. Such capabilities are expected to enable a new suite of applications currently in their infancy, from real-time holographic communication and truly immersive augmented reality experiences to the robust infrastructure required for a massive Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. It marks a fundamental evolution from connecting devices to creating a pervasive sensory network.
At the core of this vision are several key technological pillars that differentiate 6G from earlier generations. The network is being designed to operate in the Terahertz (THz) spectrum, unlocking vast bandwidth for ultra-high data rates. Furthermore, 6G is set to feature a deep, native integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), which will be critical for predictive network optimization, autonomous systems, and sophisticated data processing. This AI-native fabric will also enable the network itself to act as a sensor, providing high-precision localization and environmental awareness that will power advanced applications in logistics, autonomous transport, and public safety.
2. A Landscape of Global Competition and Collaboration
The pursuit of 6G has ignited a concerted global effort, with distinct strategic approaches emerging across continents. The Middle East, particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia, is positioning itself as a leader by leveraging its robust 5G infrastructure as a launchpad for next-generation research and trials. In Europe, collaborative projects like Hexa-X-II, led by major industry players, aim to develop a comprehensive platform for future networks, with a strong emphasis on integrating environmental sustainability into the technology’s core design.
Simultaneously, significant advancements are being made in Asia, where Chinese researchers have demonstrated breakthroughs in satellite-to-ground laser communications, a critical component for achieving truly global 6G coverage. In North America, the Next G Alliance is coordinating a roadmap to advance regional leadership in wireless technology. Despite this competitive landscape, private sector collaboration remains pivotal. Alliances focused on integrating AI into radio access networks bring together industry giants to solve common technical hurdles, underscoring a shared understanding that interoperability and global standards are essential for success.
3. The Standardization Roadmap and Emerging Business Frontiers
The path to commercial deployment is being paved by a structured standardization process, with 2025 marking a critical inflection point. The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is officially beginning the study and design phase of 6G technology, launching the first study items in Release 20, with Release 21 dedicated to defining system requirements and performance targets. The development of the new 6G radio interface is scheduled to commence, focusing on incorporating new frequency bands like centimeter-wave and sub-terahertz to meet the immense bandwidth demands of future applications.
The primary market drivers for 6G are its ability to support revolutionary applications that will redefine entire industries. Central to this vision is the concept of “digital twins”—real-time virtual replicas of physical systems that will enable sophisticated planning, simulation, and automation in manufacturing, healthcare, and urban planning. Another transformative concept is the Internet of Senses (IoS), which aims to merge the physical and digital realms through multisensory interactions. For business leaders, these advancements signal a shift toward new service-based models built on immersive experiences, hyper-automation, and data-driven environmental intelligence.
Reflecting on the Blueprint for a Connected Future
The global journey toward 6G was ultimately shaped by a complex interplay of strategic competition and indispensable collaboration. The foundational work undertaken established not only a technological trajectory for the 2030s but also a clear imperative for enterprises and nations to secure their position in a future underpinned by intelligent connectivity. This intensive period of research and standardization shifted the industry’s focus from mere speed enhancements to the deliberate creation of a secure, sustainable, and deeply integrated digital world.