The vast, interconnected network of devices that quietly reshapes our daily experiences and global industries has moved from a speculative concept to an undeniable reality, becoming a foundational technology that underpins the modern world. This ecosystem, known as the Internet of Things (IoT), is no longer an optional upgrade but a standard, integral component of how the physical and digital worlds interact. By weaving a digital layer over our environment, it has become the silent engine driving profound transformations in everything from personal convenience to large-scale industrial operations, setting the stage for the next wave of economic and societal evolution.
The Transformation of Personal and Urban Spaces
Revolutionizing the Home and Personal Well-being
The impact of IoT extends deeply into the consumer sphere, where it is ushering in new levels of convenience and personalization that are rapidly becoming mainstream expectations. At home, smart appliances are transforming domestic life into a seamless, automated experience. For instance, a refrigerator can now monitor its contents, generate recipes based on available ingredients, alert users to expiring food, and automatically add essentials like milk to a digital shopping list. Integrated systems, often orchestrated by voice assistants, allow for the control of lighting, thermostats, and security systems from anywhere in the world. A smart doorbell can provide the ability to see and communicate with visitors remotely, while automated locks grant temporary access to trusted individuals. This network of connected devices transforms a house into a responsive environment that adapts to its occupants’ needs, optimizing comfort, security, and energy efficiency without requiring constant manual intervention, thereby redefining the very concept of a modern home.
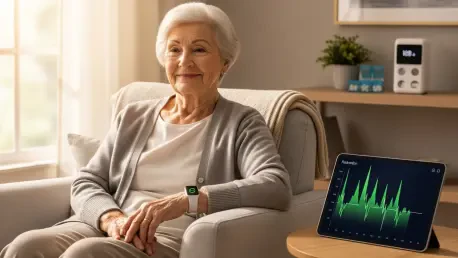
Beyond mere convenience, IoT is making significant inroads into personal health and wellness, offering proactive and preventative care solutions that were once confined to clinical settings. Wearable devices continuously monitor a wide array of vital signs, including heart rate, sleep patterns, blood oxygen levels, and physical activity. This data is then analyzed by sophisticated algorithms to provide personalized advice on everything from optimal sleep schedules to tailored exercise regimens. For individuals managing chronic conditions, these devices offer a lifeline. Remote patient monitoring systems allow healthcare professionals to track a patient’s condition in real time, receiving alerts for any concerning fluctuations. This capability is particularly transformative for elderly individuals, enabling them to live independently at home for longer while ensuring their safety. The continuous stream of real-time data provided by these IoT devices can significantly reduce hospital readmissions and empower individuals to take a more active role in managing their own health, marking a fundamental shift from reactive to preventative healthcare.
Building the Smart Cities of Tomorrow
The Internet of Things serves as the essential technological backbone for the development and management of smart cities, where interconnected sensor networks are being leveraged to address the complex challenges of growing urban populations. Cities like Singapore, Barcelona, and Amsterdam are at the forefront of this revolution, using IoT to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable environments. These systems are used to dynamically manage traffic flow, with sensors embedded in roads monitoring congestion and adjusting traffic light signals in real time to optimize vehicle movement. In the realm of public services, smart waste management systems deploy sensors in public bins to signal when they are full, allowing sanitation departments to optimize collection routes. This data-driven approach has been shown to reduce vehicle traffic from waste collection trucks by as much as 50%, saving fuel, reducing emissions, and minimizing disruption for residents. This intelligent infrastructure allows municipal governments to make better-informed decisions based on real-world data rather than historical averages.
The benefits of a connected urban infrastructure extend directly to the quality of life for residents and promote long-term environmental sustainability. Smart streetlights, for example, do more than just illuminate roadways; they conserve significant amounts of energy by dimming when no one is present and brightening upon the approach of pedestrians or vehicles. Many are also equipped with sensors that can monitor environmental factors like air quality, noise levels, and even detect gunshots, providing valuable data for public health and safety initiatives. This interconnected infrastructure leads to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies for city governments, but its true value lies in creating a more responsive and safer urban experience. By providing real-time information about public transit, parking availability, and local environmental conditions, smart city platforms empower citizens to navigate their environment more effectively, fostering a stronger sense of community and a healthier relationship with their urban surroundings.
The Economic Engine of Industry 4.0
Driving Unprecedented Efficiency Across Sectors
One of the most immediate and quantifiable benefits of widespread IoT adoption is its capacity to drive efficiency at an unprecedented scale, systematically eliminating waste in time, energy, and material resources across numerous industries. Within the industrial sector, this is most clearly demonstrated through predictive maintenance. By embedding connected vibration, temperature, and wear sensors into critical machinery, companies can monitor the real-time health of their equipment. These sensors allow machinery to signal its status and predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach prevents catastrophic breakdowns, reduces unplanned downtime by as much as 50%, and extends the operational life of vital assets. This shift from a reactive to a predictive maintenance model is already generating billions of dollars in annual returns for major corporations, transforming manufacturing floors into highly optimized, self-regulating ecosystems where operational continuity is maximized and costly disruptions are minimized.
This drive for efficiency is not limited to manufacturing; it is also revolutionizing sectors like agriculture, where resources are precious and margins are thin. IoT-powered solutions are enabling a new era of precision farming. Soil moisture meters, weather-responsive irrigation systems, and drone-based crop monitoring provide farmers with a granular, real-time understanding of their fields. This data allows for the precise application of water, fertilizer, and pesticides only where and when they are needed, optimizing resource usage and enhancing crop yields. For instance, intelligent irrigation can save up to 30% of water, a vital resource in many parts of the world. By systematically targeting inputs and monitoring crop health, farmers can increase productivity while simultaneously reducing their environmental footprint. These advancements are not theoretical gains but are already being implemented on farms globally, demonstrating IoT’s power to address fundamental challenges related to food security and sustainable resource management.
Redefining Entire Industries from the Ground Up
The influence of IoT extends beyond improving existing processes; it is fundamentally reinventing the operational models of numerous key industries, creating new value propositions and revenue streams. In logistics and the supply chain, the technology enables a level of visibility and control that was previously unattainable. Real-time tracking of shipments provides critical data points such as location, temperature, humidity, and shock detection. This is especially crucial for cold-chain monitoring, which guarantees the safe transport of sensitive goods like vaccines, pharmaceuticals, and perishable foods by ensuring they remain within a specific temperature range throughout their journey. This capability not only reduces spoilage and loss but also enhances regulatory compliance and builds consumer trust. The result is a more resilient, transparent, and efficient supply chain that can respond dynamically to disruptions and meet the growing demands of the global economy for timely and reliable deliveries.
Similarly transformative impacts are being felt across the energy, retail, and automotive sectors. In energy, the implementation of smart grids powered by IoT sensors allows for the real-time balancing of electricity supply and demand. This is crucial for the efficient integration of intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar and for preventing widespread blackouts by rerouting power during peak demand or system failures. In retail, in-store beacons and smart shelves provide real-time inventory monitoring and enable the delivery of personalized promotions directly to a customer’s smartphone as they navigate a store, bridging the gap between the physical and digital shopping experience. Perhaps most profoundly, the development of connected and autonomous vehicles relies heavily on IoT for vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication, creating the foundation for a future with significantly safer roadways and reimagined urban mobility.
The Technological Core and Its Future Hurdles
The Powerful Alliance of IoT, AI, and Big Data
The transformative potential of IoT is fully realized through its critical synergy with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data. IoT devices function as the “sensory organs” of the digital world, generating a continuous and massive stream of real-world data that serves as the lifeblood for modern machine-learning algorithms. This constant data flow from billions of endpoints—capturing everything from factory floor temperatures to traffic patterns—provides the rich, varied input that AI models require to learn, adapt, and make intelligent predictions or decisions. Without this raw material, AI would remain largely theoretical, unable to effectively interact with and optimize the physical world. This symbiotic relationship creates a powerful feedback loop: IoT provides the data, AI processes it to derive insights, and those insights are then used to control or influence IoT devices to achieve a desired outcome, creating smarter, more autonomous systems.
Further amplifying this synergy is the concept of edge computing, a decentralized approach where data processing occurs on or near the IoT device itself, rather than in a centralized cloud. This architectural shift dramatically reduces latency and bandwidth requirements, enabling the real-time responses necessary for a host of critical applications. For example, in a smart factory, a robot equipped with edge computing capabilities can autonomously detect a quality defect on an assembly line and adjust its own operations in milliseconds, without waiting for instructions from a remote server. Similarly, a connected vehicle can process sensor data locally to brake faster than a human driver could react, a capability that is essential for collision avoidance systems. By bringing intelligence closer to the source of data generation, edge computing makes IoT systems more robust, responsive, and capable of functioning reliably even with intermittent connectivity, paving the way for the next generation of truly autonomous technologies.
A New Framework for a Digital Reality
The debate over whether the Internet of Things was important had effectively concluded. By 2026 and beyond, it established itself as the default framework for interaction between the physical and digital worlds, silently revolutionizing everything from the way a coffee machine communicated with an alarm clock to how a wind turbine adjusted its performance based on distant weather patterns. The central question shifted from “if” to “how”—specifically, how to scale this powerful technology rapidly, responsibly, and ethically. The nations, cities, and corporations that successfully addressed the complex issues of security, standardization, and equitable access were the ones that reaped the most substantial benefits. They mastered the delicate balancing act required to lead the next stage of technological and economic advancement, setting a new standard for a seamlessly connected and intelligent world.